SMART Model: Overview & Best Practices
The SMART model is no longer a novel term for businesses today. Thanks to its simple but equally effective ease of use, the SMART model has shown its high applicability for businesses today.
To help you have a more detailed view of building goals with a Smart model, Fieldcheck has summarized some important information about the model in today's article. Discover now!

SMART model is no longer a novel term for businesses today
What Is The SMART Model?
Regarding the question of what the SMART model is, it can refer to one of the ways to help organizations and businesses build and evaluate the rationality and feasibility level when implementing the goals in the original plan.
Not only that, but SMART also supports determining which goals are suitable for business strategies at many times. The Smart diagram represents the following criteria
- S - Specific
- M - Measurable
- A - Attainable
- R- Relevant
- T - Time Bound

SMART supports determining which goals are suitable for business strategies
Benefits of the SMART Model Application in Marketing
What are SMART goals? This model brings many benefits for businesses, especially in the marketing segment, as follows:
#1. Concretize The Goals
When completing a quarter, the management levels and staff will often set new goals for the next quarter. Organizations and businesses often build large and high expectations. However, these goals, in reality, are still vague and not feasible.
The SMART method can help businesses solve the situation by assisting managers in determining what their goals are specific through specific measurement indicators. Through this, companies will produce a picture of clear and specific goals.
#2. Increase Accuracy And Suitability For Goals
When using a successful SMART model, the management level can eliminate targets unsuitable for business development. Through this, businesses can better orient to conquer their goals.

The management can eliminate targets unsuitable for business development with SMART
#3. Improve The Measurement Capabilities Of The Goals
One of the other benefits of Smart is that the management level can improve the measurement of goals. Through this, the model will support the determination of the achieved results and the extent to which employees can complete the job.
#4. Increase Conformity With The Goals Of The Business
The 4th element - Relevant will be able to link the parts and departments' specific goals to the company's general purposes. This link helps connect and connect businesses and supports collective strength to face difficulties.
#5. Improve Work Efficiency
The SMART model supports the staff according to the orientation set out in the work process toward a more specific goal. Not only that, employee working results help measure and evaluate the target correctly when the SMART model management levels.
How To Determine The Goal According To The SMART Rules
There are 5 factors when choosing the target by SMART:
#1. Specific
The more specific and clear goals, the more SMART help businesses identify and measure the feasibility of activities.
On the contrary, when you only summarize the goals generally, the management level is difficult to grasp and measure the feasibility level of the work done to see if it is right with the plan.

SMART helps businesses identify and measure the feasibility of activities
#2. Measurable
The goals in work should be attached to specific numbers. When businesses set goals according to the Smart model's measurable factor, they will show their ambition.
In addition, when setting goals for work, businesses need to determine whether they can do it. After achieving goals, companies can measure the effectiveness to evaluate the results according to specific and practical numbers.
#3. Attainable
One of the other important criteria of the SMART business model is the feasibility of goals. Therefore, the management should consider the possibility of achieving those goals. When the plans are feasible, the management may be motivated to try and exceed their limits.

The management should consider the possibility of achieving overall goals
#4. Relevant
One of the other important factors when determining the goal for the Smart model is practicality. In other words, you need to determine whether your personal goals are related to the general development orientation of the business.
In addition, you need to evaluate whether the set goals meet the problem you are having before implementation.
#5. Time Bound
Setting deadlines for completing goals can create pressure on members to meet deadlines. This action will help improve discipline and, at the same time, increase productivity for employees in the company.

Setting deadlines for tasks can motivate employees to work better
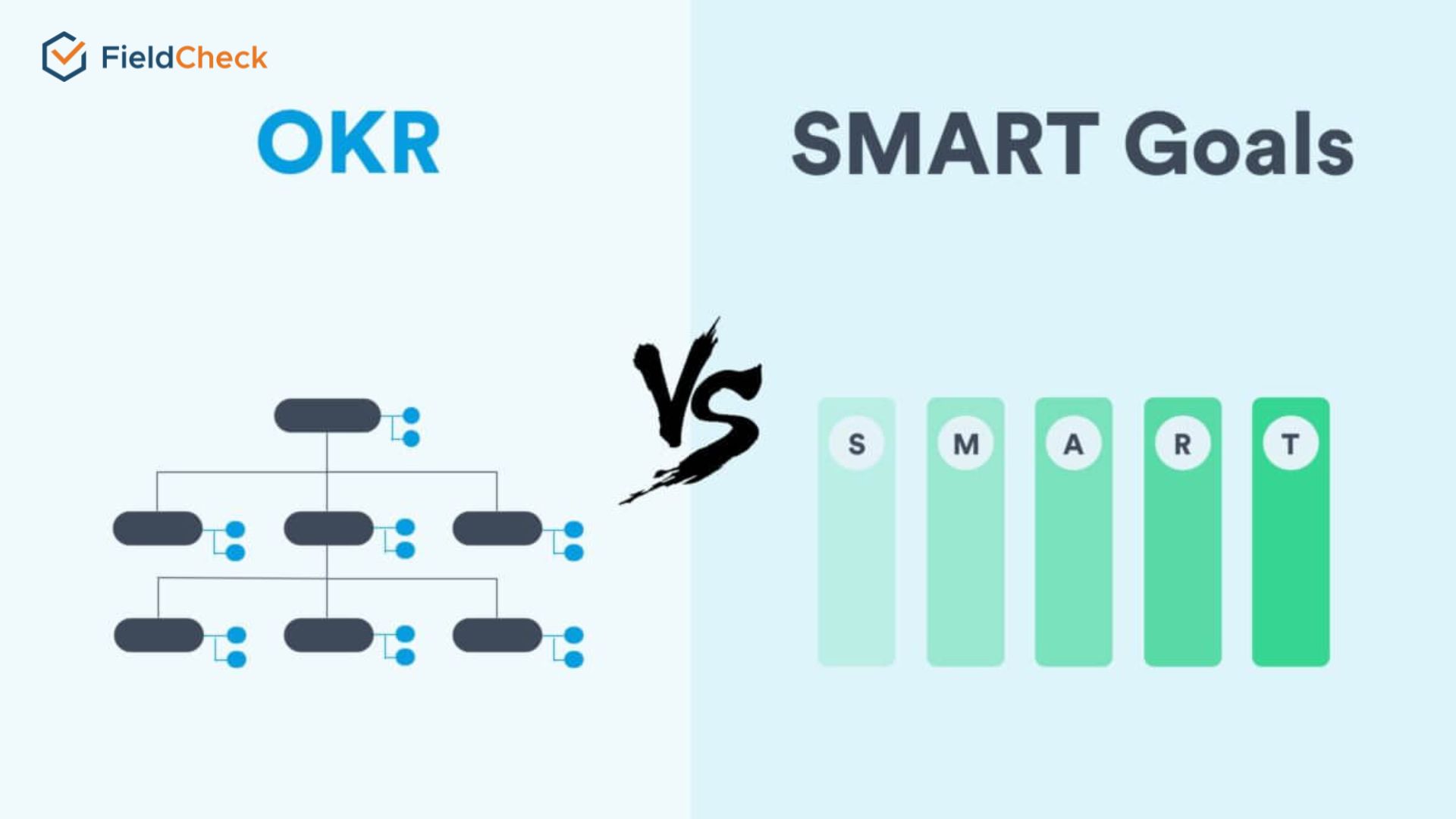
Difference Between OKR and SMART Model
The SMART and OKR models are quite similar. They possess a clear model structure regarding time, the combination of goals, and the scope of goal implementation.
While SMART sets individual goals in a simple and easy-to-remember manner, OKRs can clearly distinguish between Objectives (the desired achievement) and ways to measure effectiveness in achieving those goals by key results.
In this regard, the letter M in SMART is also easily confused because it can mean many different things, such as Measurable, Motivational, and Meaningful.
Changing the meaning to another M can change the structure and goals of the SMART model. This can reduce the importance of measurability, while the OKR model can ensure this compared to the SMART model.
The biggest difference between the OKR and the SMART model is the ability to set goals according to different time frames and tiers.
Original OKRs hold first place in the OKR hierarchy, lasting 5-10 years. The above goal serves the vision and mission of the business (what is the company's purpose after the above time?).
OKR and SMART are proved their effectiveness in helping companies improve operating efficiency
Enterprise OKRs are considered level 2 and last for about a year. This model represents the enterprise's strategies, expressed through 3 - 5 proposed goals.
OKRs play an important role in helping to connect all activities in businesses, companies, and organizations. This model also helps to define a clear focus for all employees.
OKRs of the department belongs to the 3rd level in the diagram. This level is usually set for a quarter of a year. It can represent the strategy departments, and divisions take to conquer the business OKRs, or the second and ultimately original OKRs.
Compared with the SMART planning model, OKR can provide a full picture of the goal - the level of the business and the organization, as well as the relationship between the plans at that level. SMART will focus primarily on individual goal setting.

SMART example (Source: Hubspot)
SMART Goal Setting Examples
There are many examples of SMART model for goal setting in various fields such as business, marketing, human resources, etc. There is even a SMART model in scientific research and a SMART model in learning.
Let's look at some typical examples in the following content with FieldCheck.
#1. SMART Model in Business Industry
For the SMART model in business, business A wishes to expand its share in the market. Accordingly, the management level needs to build SMART goals as follows:
- Specific - S: Expand the company's share in the market
- Measurable - M: Expand the company's share to 20% of the market share
- Attainable - A: Possessing strong financial potential and high competitiveness, the enterprise will expand its market share to 20%.
- Relevant - R: To increase the influence of the product and the business in the market.
- Time bound- T: Businesses need to complete the item before December 31, 2023.
#2. SMART Model in Marketing
The business wants to improve the search order on Google. Accordingly, the goal table according to the SMART model can be presented as follows:
Specific - S: Increase the ranking of the company's website to page 1 of Google with the keyword "task management software"
- Measurable - M: Increase the current position to the top 3 on page 1 of Google
- Attainable - A: Possessing the ability to optimize the website of the current Marketing team, the business will increase the website ranking to the top 3 on page 1 of Google with the keyword "task management software"
- Relevant - R: To reach potential customers who are in need of task management software.
- Time bound - T: Enterprises need to achieve their goals before December 31, 2023.
 SMART example (Source: Hubspot)
SMART example (Source: Hubspot)
#3. SMART Model in the HR Industry
In human resources, management can also apply SMART when setting individual goals. For example, the department wants to improve the company's employee attendance process.
- Specific - S: Time attendance is more accurate and convenient, reducing manual work
- Measurable - M: For all employees of the business
- Attainable - A: With the capacity and experience of the current human resources team, businesses want accurate and convenient timekeeping, reducing manual work for all enterprise employees.
- Relevant - R: To ensure comfortable working for members of the enterprise
- Time bound - T: Before the 31st of every month
Wrapping Up
Above is some information related to the SMART model and typical examples. In general, if OKRs show the overall picture between goals, the SMART model helps businesses to set individual goals clearly and specifically.
Depending on the nature and characteristics of the business, the management level can choose the appropriate model to set general and separate goals for each department.




